|
Different
methods were tested in the past: ventilation of indoor air with heat recovery,
radon-proof membranes, protective coating of the floors, etc.
Nowadays,
the sub-slab ventilation is considered the most effective system.
Principles
of designing and application of various ventilation systems are published in
CSN 730601 Protection of houses against radon from the soil.
Different
systems:
- one, or
several perforated tubes drilled beneath existing floors (from the cellar, from
an external chase, or from an internal chase);
- one, or
several radon sumps installed into the sub-floor region of the building;
- a
network of flexible perforated pipes inserted into the drainage layer of coarse
gravel placed beneath the floors (reconstruction of floors necessary);
- a
combination of the above stated measures.
Example: old house with extremely high indoor radon
concentrations
parameters of the ground
cA75 = 71 kBq.m-3
k75 = 1.6 10-11 m2
RP (radon potential) = 88
high radon index
average indoor radon values: about 35000 Bq.m-3 in habitable rooms; 77000 Bq.m-3 in the cellar
indoor radon concentration in the cellar was the same as the
soil-gas radon concentration in the surroundings of the building
very fast changes of indoor radon concentration were observed
Remedial measures were realized in 2005:
sub-slab ventilation and reconstruction of floors in almost all
rooms;
sub-slab ventilation system consists of two independent sections
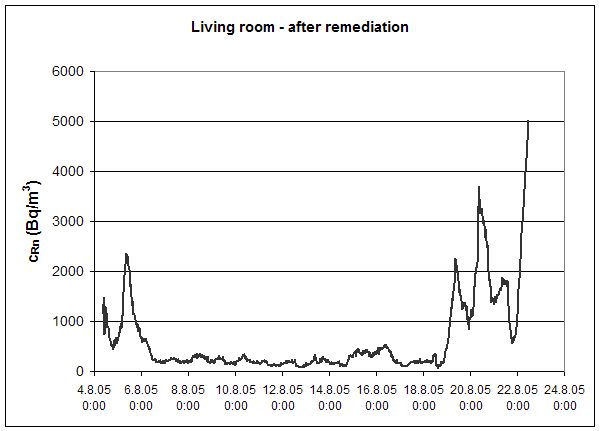
ventilation
experiment:
4.8.
8.45 - 11.8. 9.30
gradual
start of the 1st section
11.8.
9.30 - 18.8. 10.15
both
sections in operation (maximum power)
18.8.
10.15 - 22.8. 12.00
ventilation
switch-off
|